The Structures That Connect Cardiac Muscle Cells Are
The resulting mRNA gives rise to a 151 amino acid polypeptide known as preproANP. The myofilaments within the myocyte are surrounded by sleeves of sarcoplasmic reticulum analogous to endoplasmic reticulum found in other cells.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Anatomy And Physiology
3 4 The latter serve as temporary scaffolds mechanically supporting the cells and promoting their.

. Cardiac muscle is striated although the pattern is not as ordered as in skeletal muscle. Smooth muscles also called involuntary muscle such as the muscles contained in the stomach and other internal organs like the female uterus. They connect directly with the sarcolemma at one end before travelling deep within the cell forming a network of tubules with sections running both perpendicular transverse to and parallel axially to the sarcolemma.
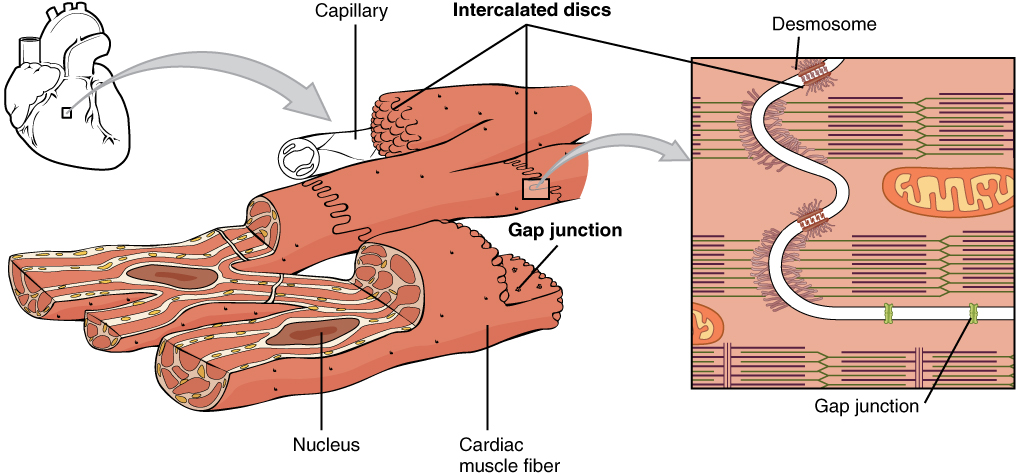
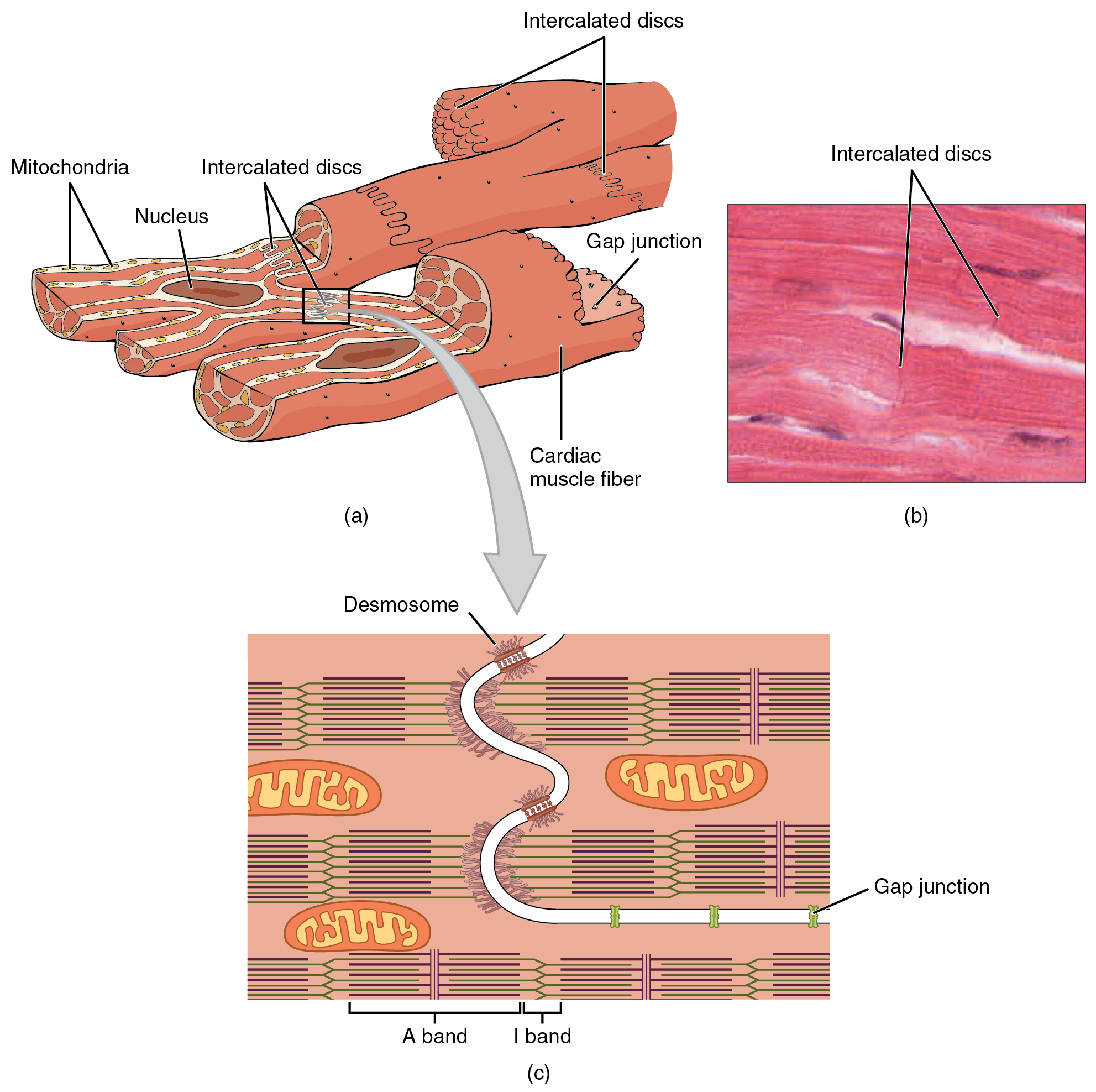
Desmosomes are other structures. 21 Atrial Natriuretic Peptide. Like skeletal muscle cells cardiocytes have a striated appearance but their overall structure is shorter and thicker.
T-tubules are tubules formed from the same phospholipid bilayer as the surface membrane or sarcolemma of skeletal or cardiac muscle cells. The inner endocardium lines the cardiac chambers covers the cardiac valves and joins with the endothelium that lines the. A Cardiac muscle cells have myofibrils composed of myofilaments arranged in sarcomeres T tubules to transmit the impulse from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell numerous mitochondria for energy and intercalated discs that are found at the junction of different cardiac muscle cells.
Cardiac muscle tissue or myocardium forms the bulk of the heart. 1The human gene encoding ANP is called NPPA GeneID 4878 and is located on chromosome 1 at location 1p3621NPPA is approximately 2 Kb in length and consists of 3 exons and 2 introns. Intercalated discs connect cardiac muscle cells.
2 Cardiac tissue engineering provides an alternative approach by integrating cardiac cells and 3D biomaterials. All natriuretic peptides are synthesized as preprohormones Fig. 1 shows the arrangement of the thick and thin filaments.
Gap junctions inside the intercalated discs relay electrical impulses from one cardiac muscle cell to another. These appear as the dark-staining transverse lines crossing the chains of cardiac cells. These are the specialized structures joining two cardiac myocytes.
Cardiac muscle is made from cells called cardiocytes. Since the number of cardiac donors is limited there is a need to develop new approaches to regenerate the infarcted heart. Cardiocytes are branched allowing them to connect with several other cardiocytes forming a network that facilitates coordinated contraction.
Figure 1921 Cardiac Muscle. B A photomicrograph of cardiac muscle cells. The heart wall is a three-layered structure with a thick layer of myocardium sandwiched between the inner endocardium and the outer epicardium also known as the visceral pericardium.
Cardiac muscle which makes up most of the heart wall also an involuntary muscle Nerve tissue is made up of nerve cells neurons and is used to carry messages to and from various parts of the body. However the myofibrils in cardiac muscles are less dense as compared to the skeletal muscles. Just like the skeletal muscle cells sarcomeres are the contractile units.
Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology

Cardiac Muscle Definition Function And Structure Biology Dictionary
Comments
Post a Comment